Many enterprises now use Oracle Database to support mission-critical applications. A database with high availability helps ensure business continuity. That’s why companies would also reinforce Disaster Recovery (DR) for Oracle Databases to enable quick switching during a failure or disaster, thereby avoiding business disruption.
Traditional DR solutions, however, have a number of drawbacks, including the requirement for consistency between DR and production system architecture, high cost, complex O&M, and poor flexibility and scalability. How can enterprises achieve more effective data protection at a lower price, with a simpler architecture and easier O&M?
As a leading HCI innovator, SmartX offers DR resource pool solutions tailored for Oracle Databases deployed in a variety of production environments. In this article, we will discuss how SmartX uses HCI in conjunction with Oracle Data Guard/Active Data Guard (DG/ADG) and Oracle GoldenGate (OGG) to strengthen DR for Oracle Databases. This includes solutions for three major production scenarios, as well as a financial-service use case.
Tailormade Solutions for Different Scenarios
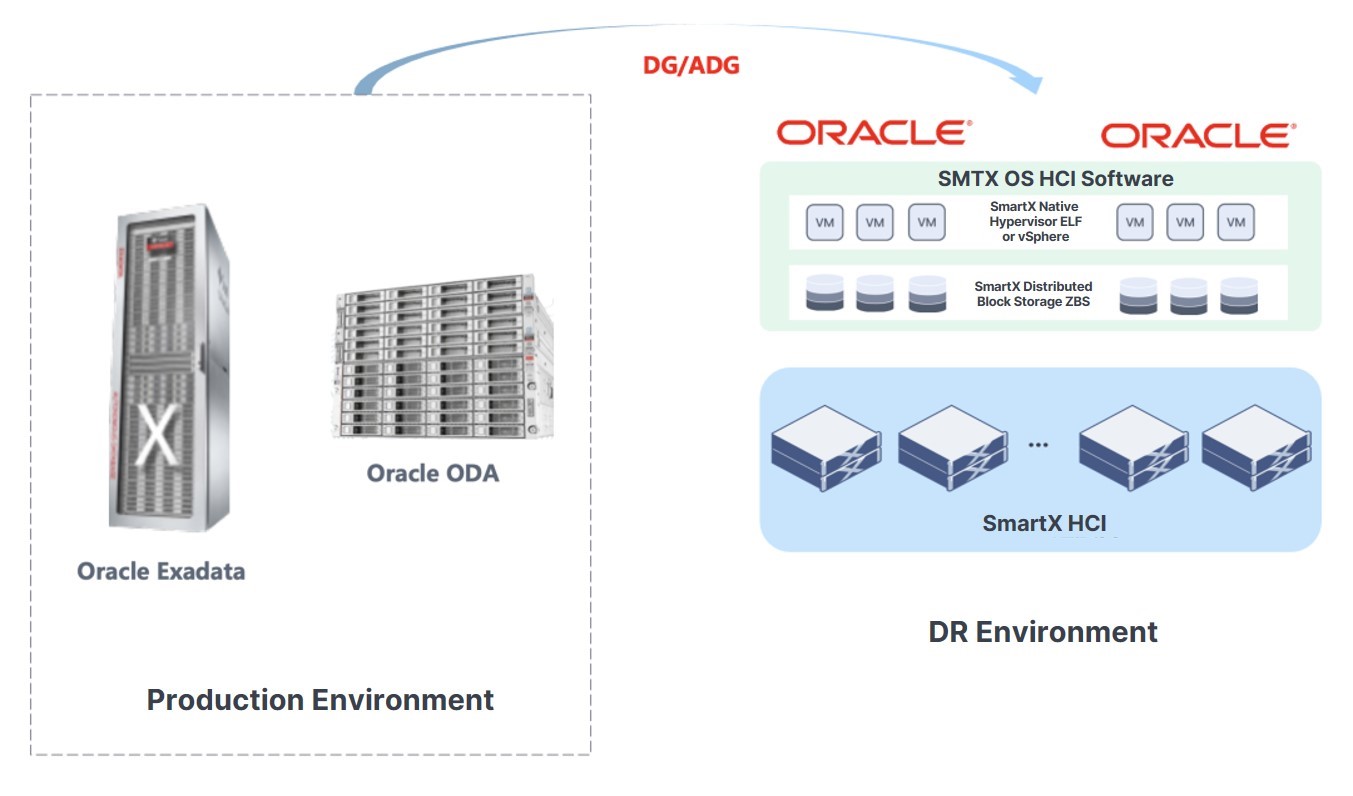
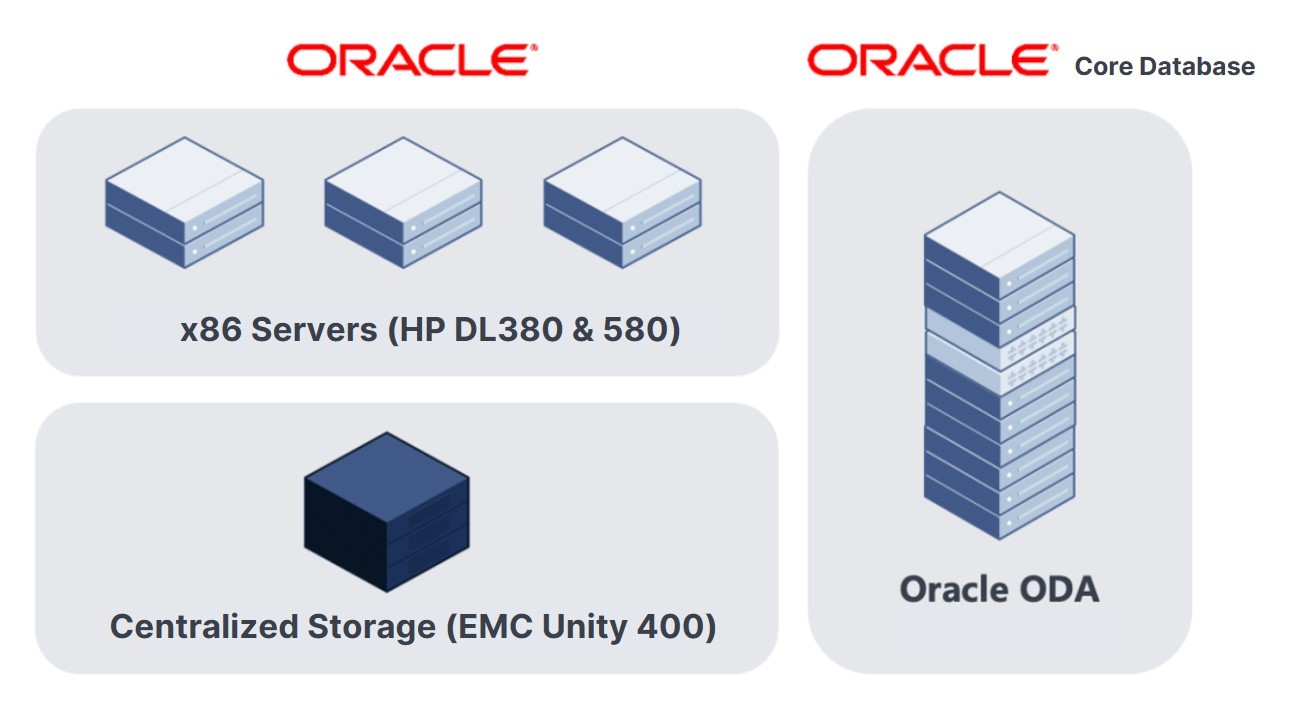
When Using Oracle Appliances in Production Environment
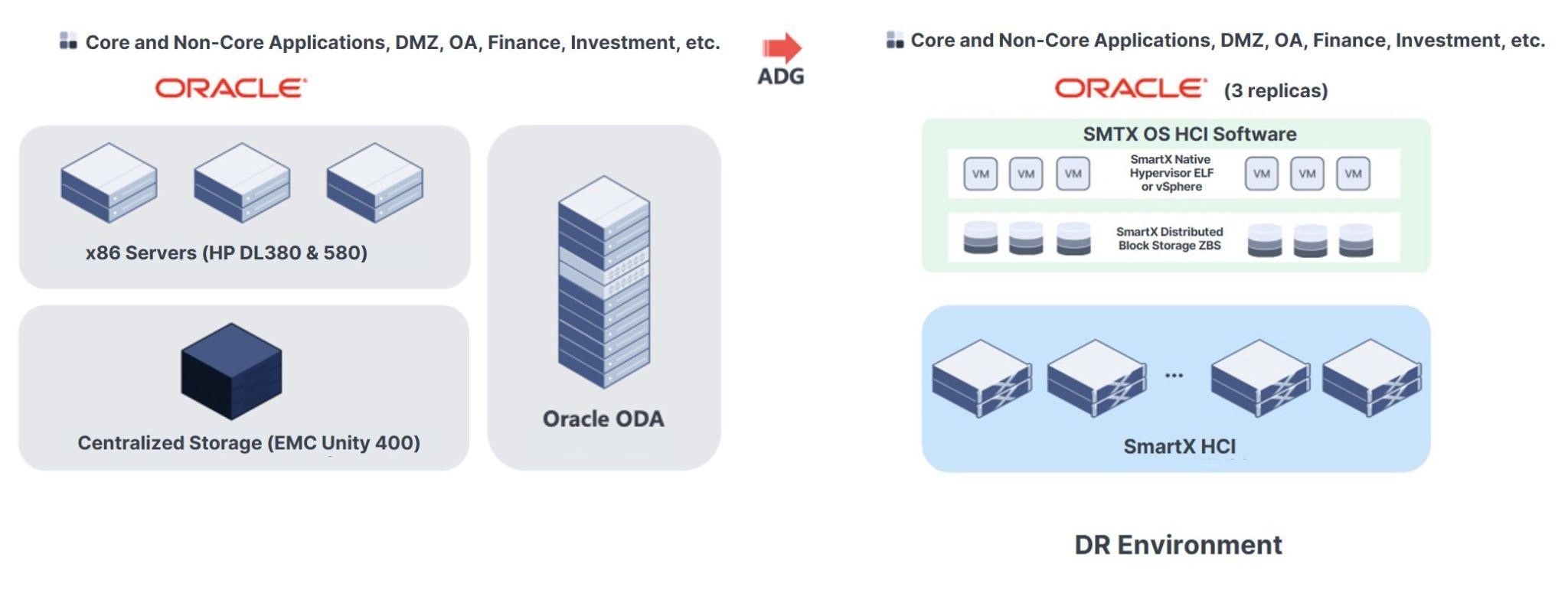
Enterprises using Oracle Exadata Database Machine or Oracle Database Appliance to run Oracle Databases may leverage Oracle DG/ADG to synchronize the production application data to the DR end supported by SmartX HCI.
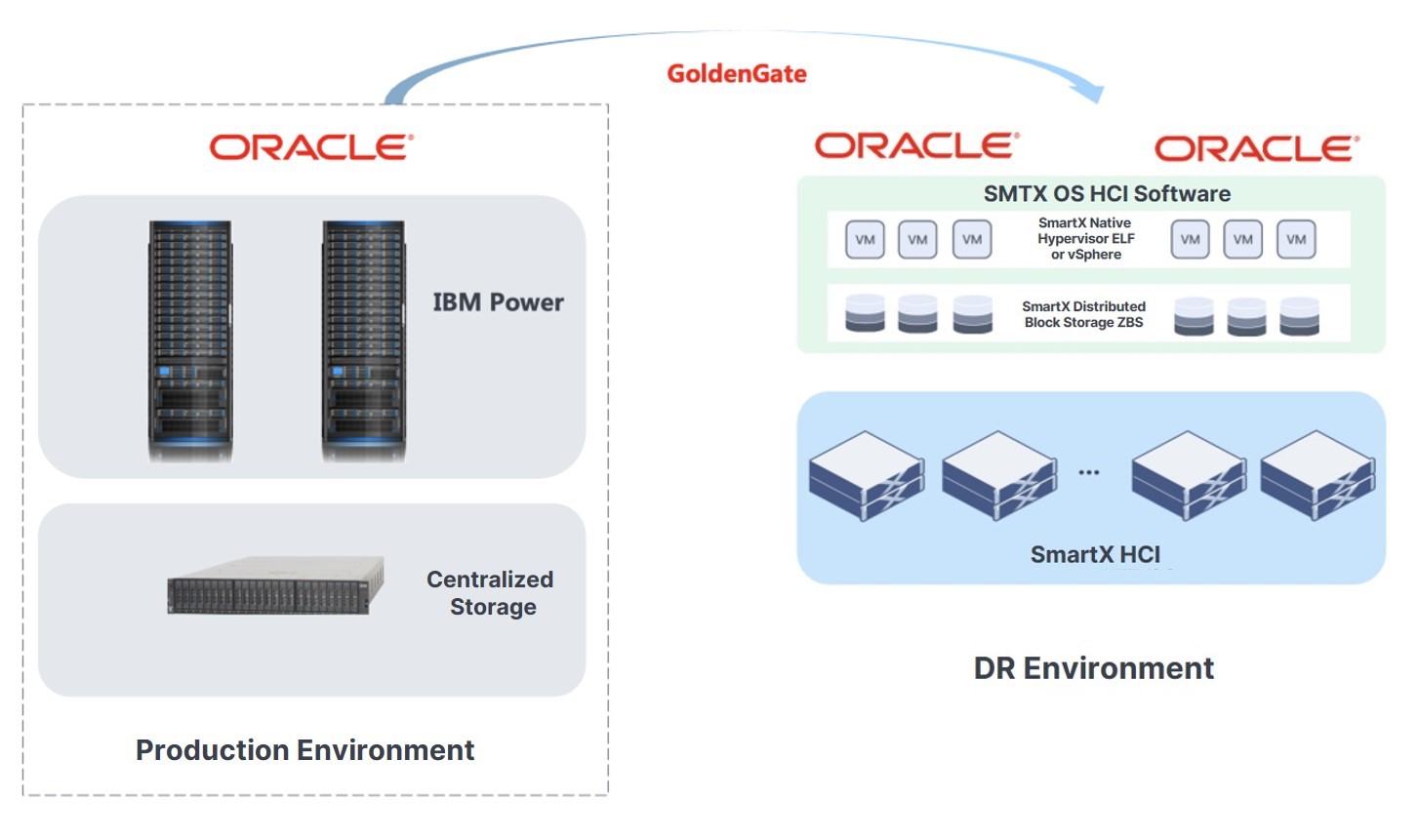
When Using IBM Power Servers with Centralized Storage
Enterprises using IBM Power Servers with centralized storage to run Oracle Databases may leverage OGG to synchronize the production application data to the DR end supported by SmartX HCI.
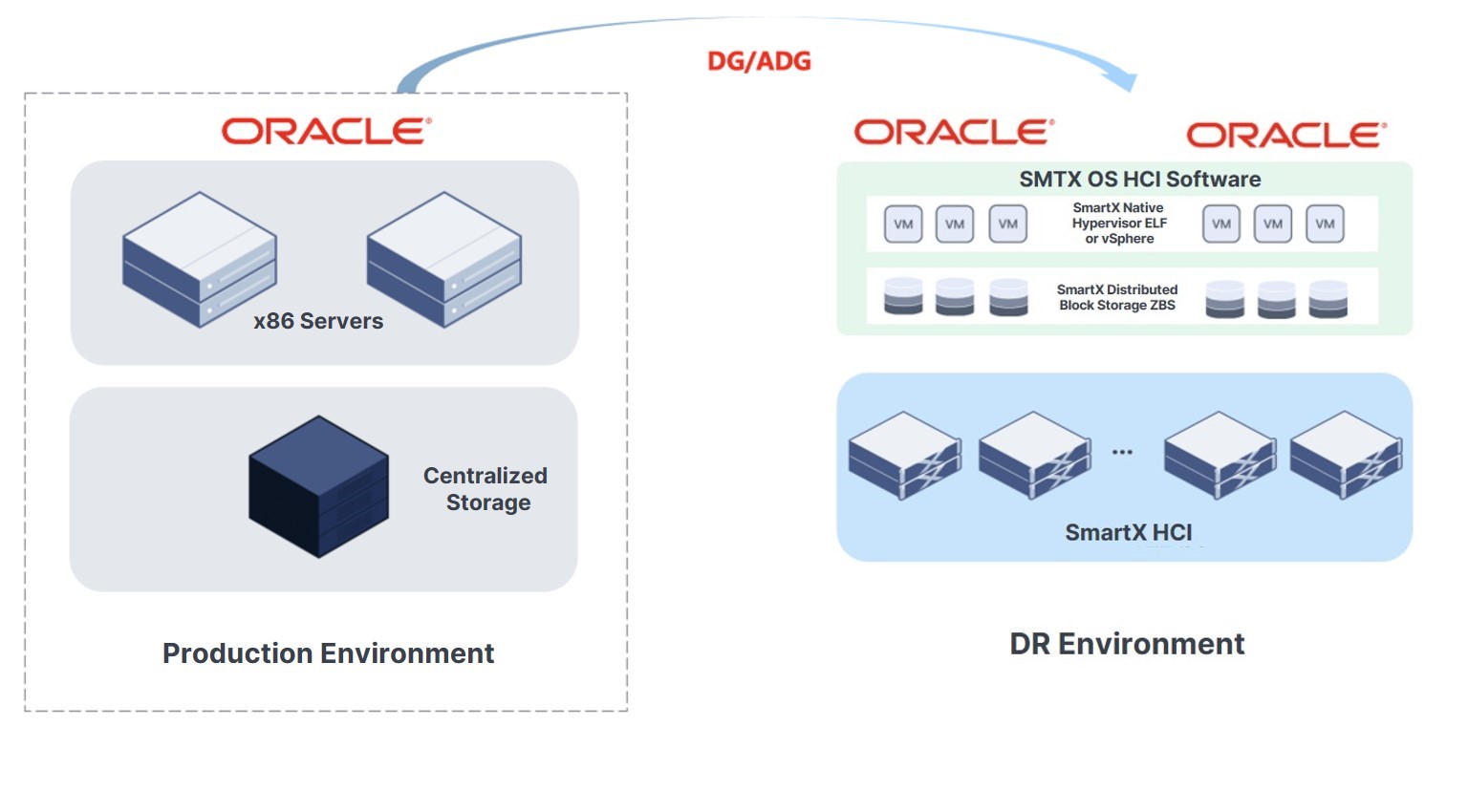
When Using x86 Servers with Centralized Storage
Enterprises using x86 servers with centralized storage to run Oracle Databases may leverage Oracle DG/ADG to synchronize the production application data to the DR end supported by SmartX HCI.
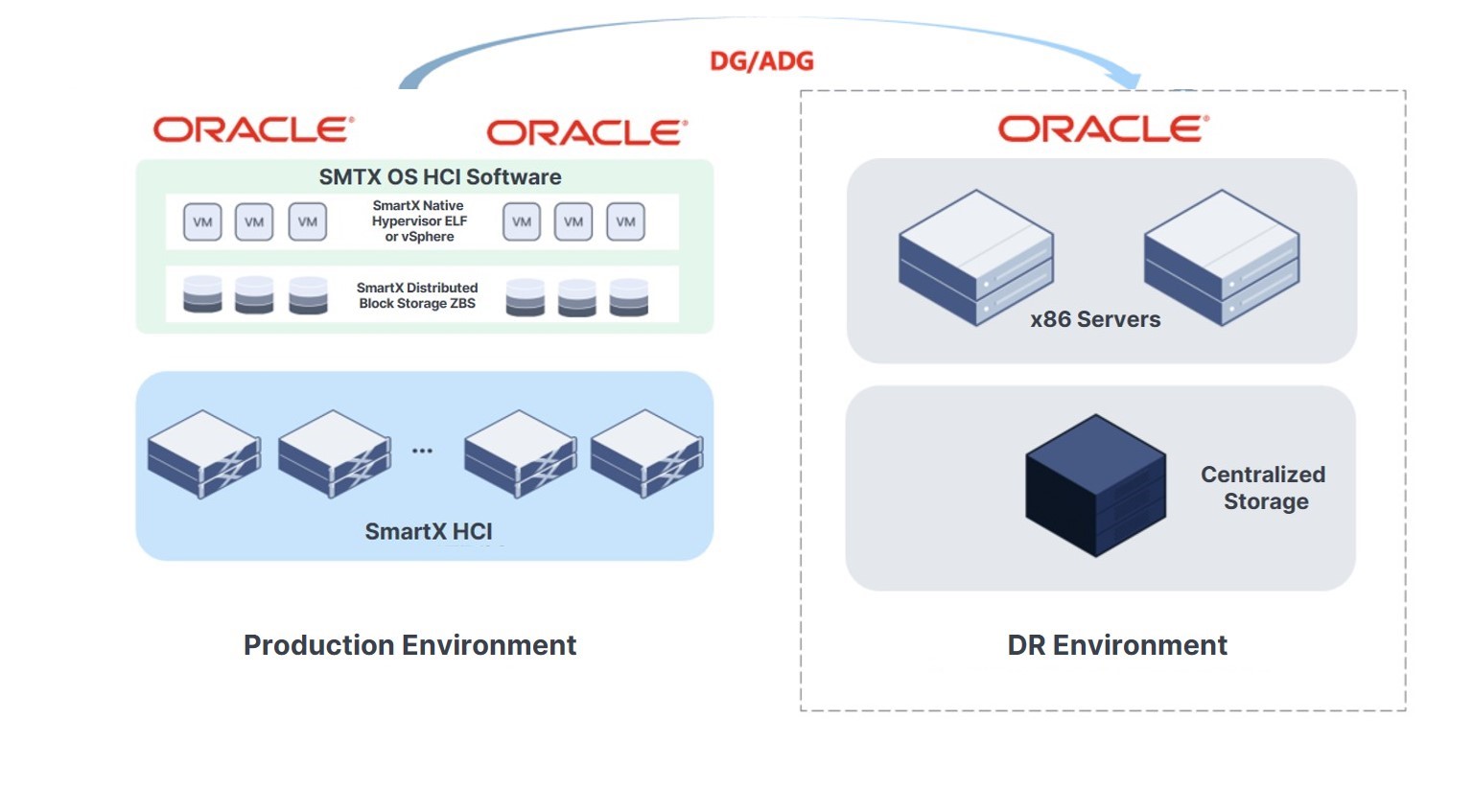
If users’ hardware devices are significantly aged or experiencing issues such as performance and capacity bottlenecks, it is recommended that production clusters be moved to the SmartX HCI platform, with legacy devices used as disaster recovery databases. Because of SmartX HCI’s optimized performance and flexible scalability, enterprises can reduce DR investment while improving business efficiency.
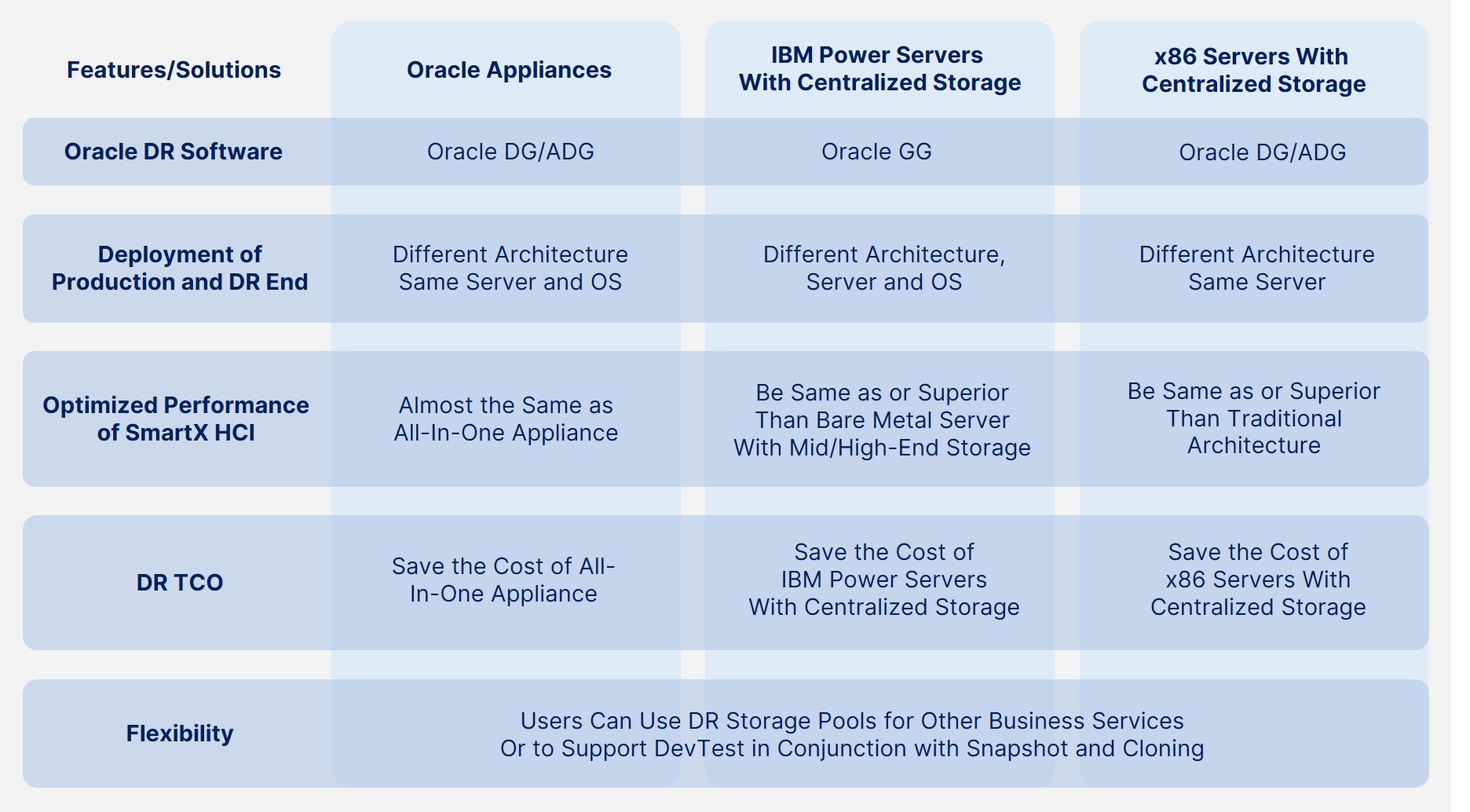
Features and Advantages
Case Study: An Insurance Company Using SmartX HCI to Reinforce DR for Oracle Database Appliances
Background
A property insurance company previously used ODA to support core-business databases and x86 bare-metal servers (with centralized storage) to support Oracle Databases of non-core applications, OA, and so on.
To improve business continuity, user decided to increase the DR capacity of the infrastructure. Due to budget constraints and low utilization of DR systems, user planned to deploy a new DR storage pool at the same location as the production clusters. Some detailed requirements include
- Infrastructure upgrades: To create a comprehensive enterprise-level IT DR system to improve business continuity and support business development.
- Capacity improvement: To improve the risk resistance capacity of the infrastructure by developing an effective DR system and emergency plan that fully leverages automated tools.
- Advanced technologies: To enable a highly reliable, agile, cost-effective, and adaptive DR solution.
Challenges
The main goal is to provide a production-level protection for Oracle Databases, which means that when a downtime occurs, the databases should be quickly switched and mission-critical applications recovered. Meanwhile, even though the DR system is rarely used, it should perform similarly to the production clusters and meet production requirements during the disaster. While these objectives can be easily met by deploying DR clusters according to the architecture of production clusters, it is more expensive and increases O&M complexity.
Solutions
After discussing the above challenges with SmartX engineers, user decided to use SmartX HCI (with VMware virtualization) to construct the DR resource pool for Oracle Databases and Oracle ADG to synchronize data from production clusters to DR clusters. This means that while the DR clusters use different architectures, they can be powered by the same CPUs and servers the production clusters, lowering overall costs while increasing the DR system’s performance, simplicity, and flexibility.
To increase the availability of the databases, the data is stored in three replicas. When an outage occurs, the databases that support mission-critical applications can be quickly switched from production to DR clusters with second-level RPO and minute-level RTO.
Outcomes
- The DR clusters increase overall utilization by providing both data-protection services and other production services.
- Achieve second-level RPO and minute-level RTO at a lower TCO, considerably improving the business continuity.
- Enable on-demand scalability and the increase of capacity and performance of power-on servers.