The hyperconverged infrastructure has gradually become a mainstream solution in the IT infrastructure market with a growing user base and increasingly dynamic application scenarios. However, due to its significant differences from legacy architectures, users unfamiliar with hyperconvergence would still raise questions like:
- What are the differences between hyperconvergence and legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure?
- How will my enterprise and data center benefit from hyperconvergence?
In this article we would answer these questions by explaining the differences between the hyperconverged and legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure. But first, what is hyperconvergence and why do we need it?
A misunderstanding: The essential of hyperconvergence
The name of hyperconvergence has created a prevalent misunderstanding that hyperconvergence is created for converging features: the more functions it converges, the more powerful it becomes. However, the truth is, hyperconvergence first and foremost involves the replacement of traditional storage with distributed storage, with many other advantages (such as x86 server-based architecture, concurrency, and scalability) coming as a result of this innovation. Thus, hyperconvergence is essentially about the converged deployment of distributed storage and virtualization.
Four differences: Comparison of architectures and resource management models
We examine the differences between hyperconvergence (here we take SmartX hyperconvergence as an example) and legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure through their architectures and resource management models.
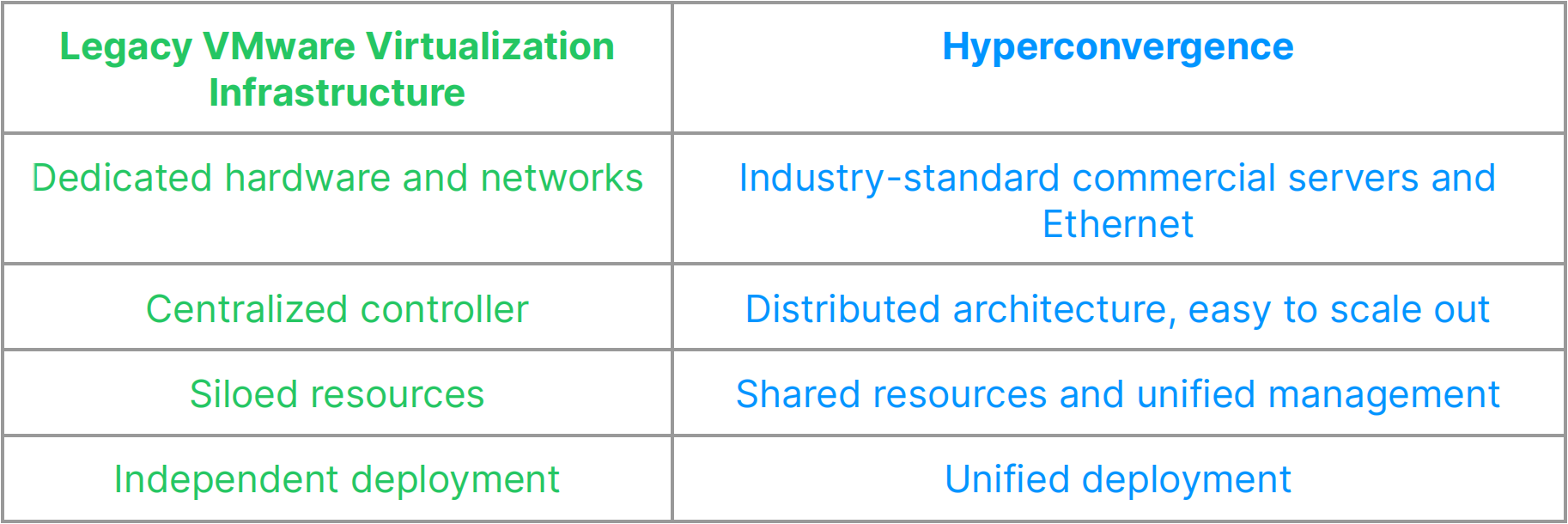
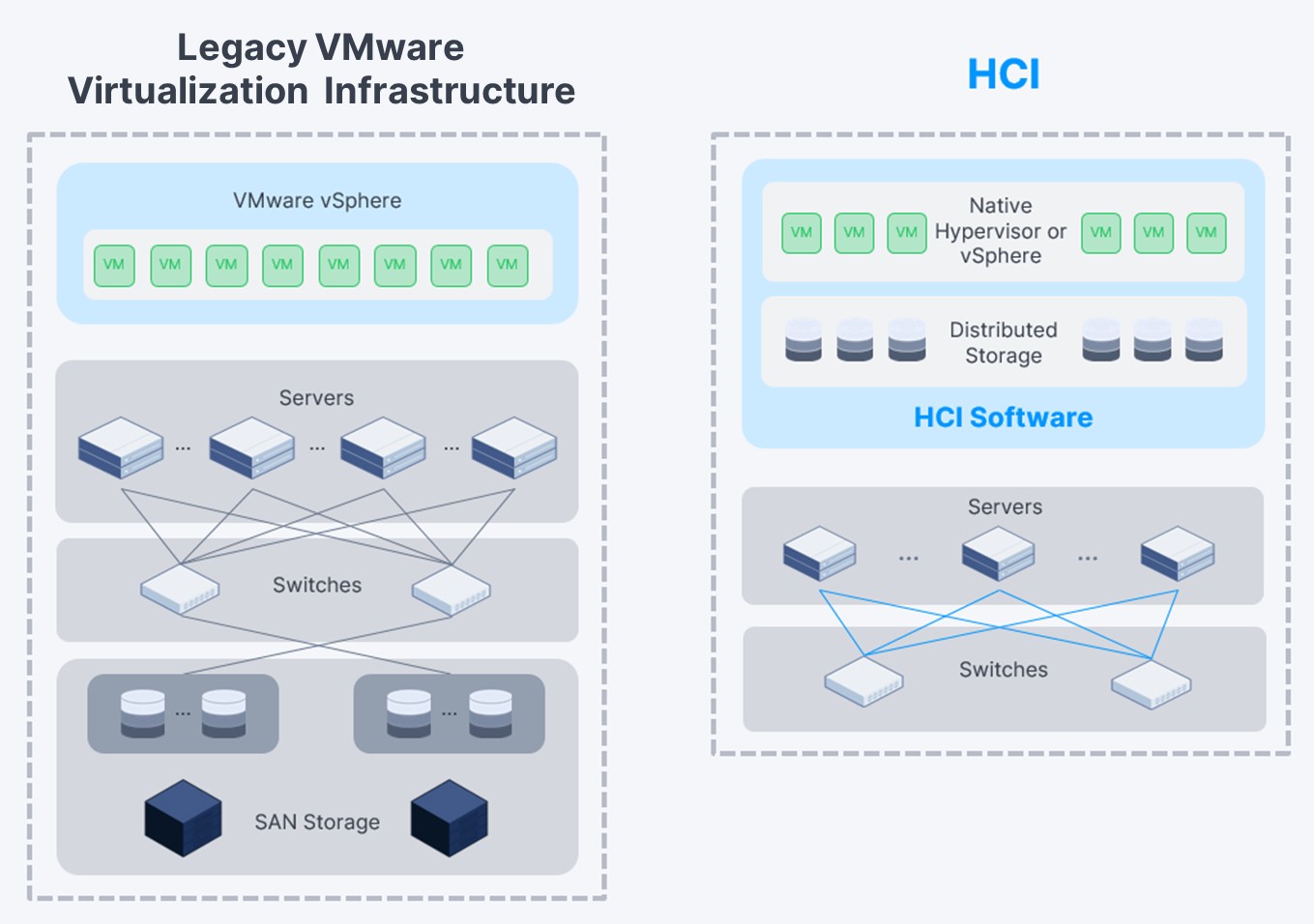 Comparison of resource management models
Comparison of resource management models
Four remarkable differences can be summarized as follows:
- Hyperconvergence does not use dedicated hardware and networks; instead, it uses industry-standard and easy-to-maintain servers and Ethernet switches;
- Hyperconvergence has distributed storage at its core, with each server serving as a storage controller. It should be noted that each of these nodes configures SSD as caches. This means that the cache capacity of distributed storage is much larger than the volatile memory in traditional storage. Meanwhile, the multi-node concurrency brings higher aggregated performance. Technically, distributed storage replaces RAID arrays with a unified and scalable resource pool. So hyperconvergence has greater scalability than legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure;
- Hyperconvergence resolves the problem of resource silo by automatically sharing, managing and balancing data in the distributed storage. This also contributes to hyperconvergence’s improvement in capacity, performance, and on-demand scalability;
- Hyperconvergence converges compute virtualization and storage and deploys them on the same server node. This means that hyperconvergence has a simpler architecture than legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure.
Five advantages: An all-rounded upgrade of IT infrastructure
Based on the differences raised above, we could obviously find that hyperconvergence comprehensively improves the IT infrastructure through distributed storage and streamlined architecture. These improvements include but are not limited to increasing reliability, concurrency, scalability and reducing operation and maintenance difficulties and costs.
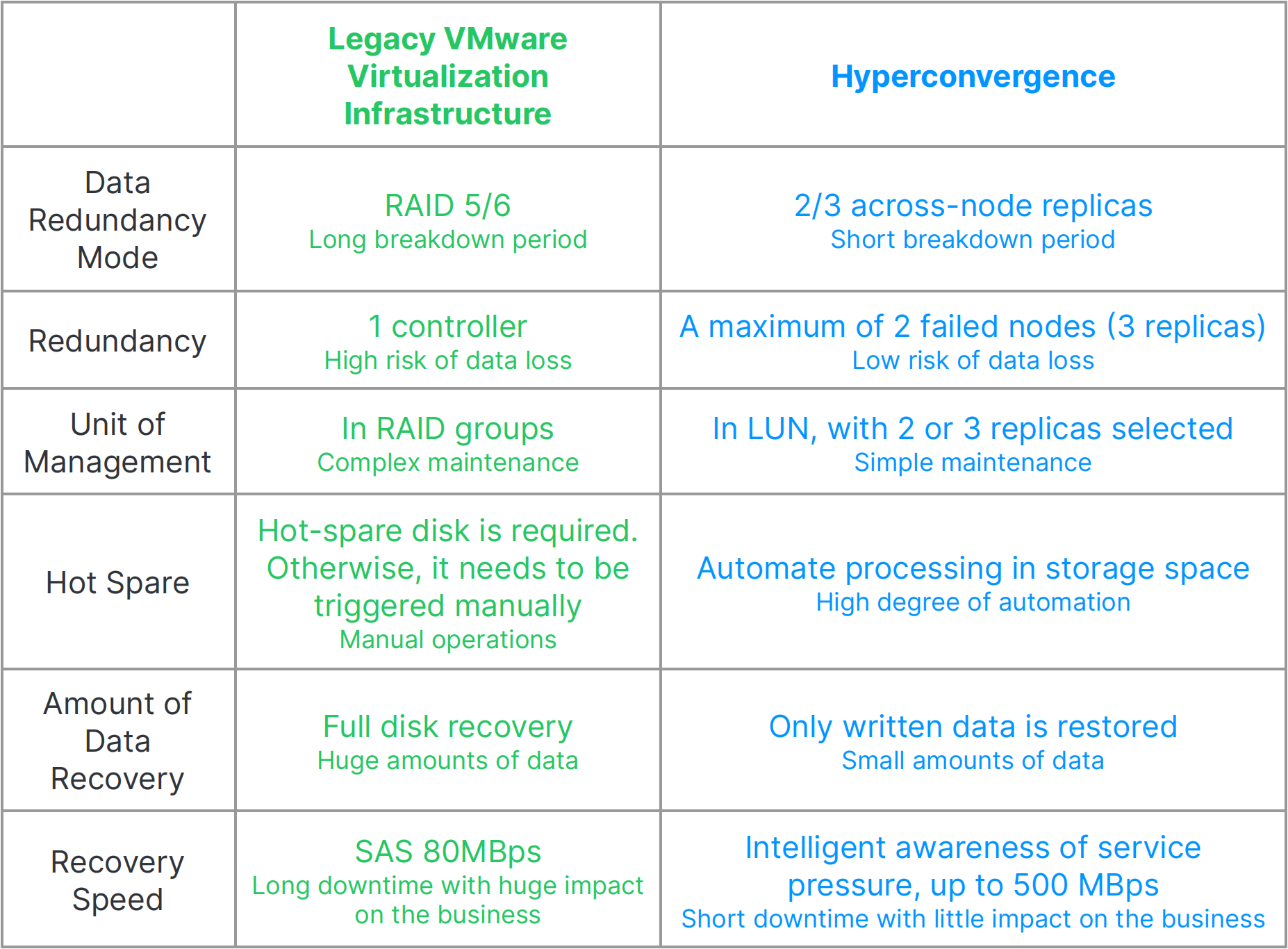
- Increased reliability
Many enterprise users have a common question about software-defined data center architectures: are x86-server-based systems reliable?
The answer can be negative at first glance because x86 servers may suffer from single points of failure. However, in hyperconvergence, servers work in clusters. Distributed storage’s multiple replications and other features also ease this concern, helping to build a large-scale system with high reliability.
In fact, hyperconvergence has many advantages over legacy VMware virtualization infrastructure in terms of reliability, as detailed below:
In addition, vendors such as SmartX, Nutanix, and VMware provide enterprise-grade storage services featuring data checksum, topology awareness, active-active cluster, cross-site replication, etc., as well as enterprise-grade high availability and data protection solutions integrated with third-party products.
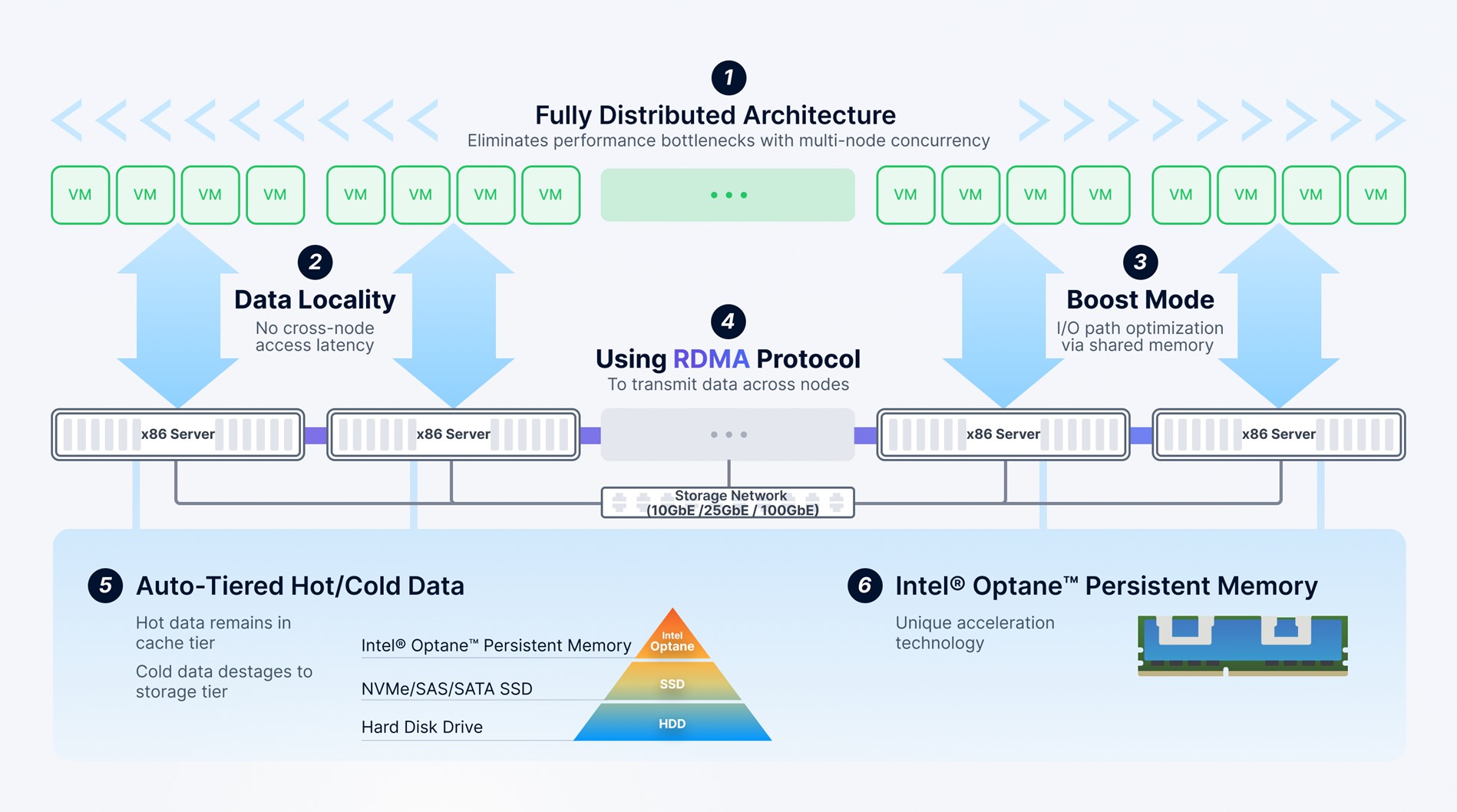
- Increased concurrency and reduced I/O latency
Below we explain how hyperconvergence enhances performance and reduces I/O latency, using SmartX’s hyperconvergence software SMTX OS as an example.
To be specific, the distributed architecture enhances the system’s overall performance. SSD caching improves single-node access capacity. And I/O locality, an exclusive advantage of hyperconvergence, further reduces I/O latency. It is also noticeable that I/O locality is mainly supported by SmartX and Nutanix, not those hyperconvergence solutions based on open-source products such as Ceph.
Here is a specific example of hyperconvergence’s high performance. Usually, it takes 8 SSDs to boost HPE 3PAR 8440 to reach its maximum IOPS. But a supervisor performance can be easily achieved with only a 3-node SmartX cluster.
- Increased scalability
As described above, distributed storage provides substantially enhanced scalability over traditional storage. Some of the features include:
Among these features, heterogeneous scalability can be offered only by a few vendors such as SmartX. Some HCI products from other vendors may not be able to support it.
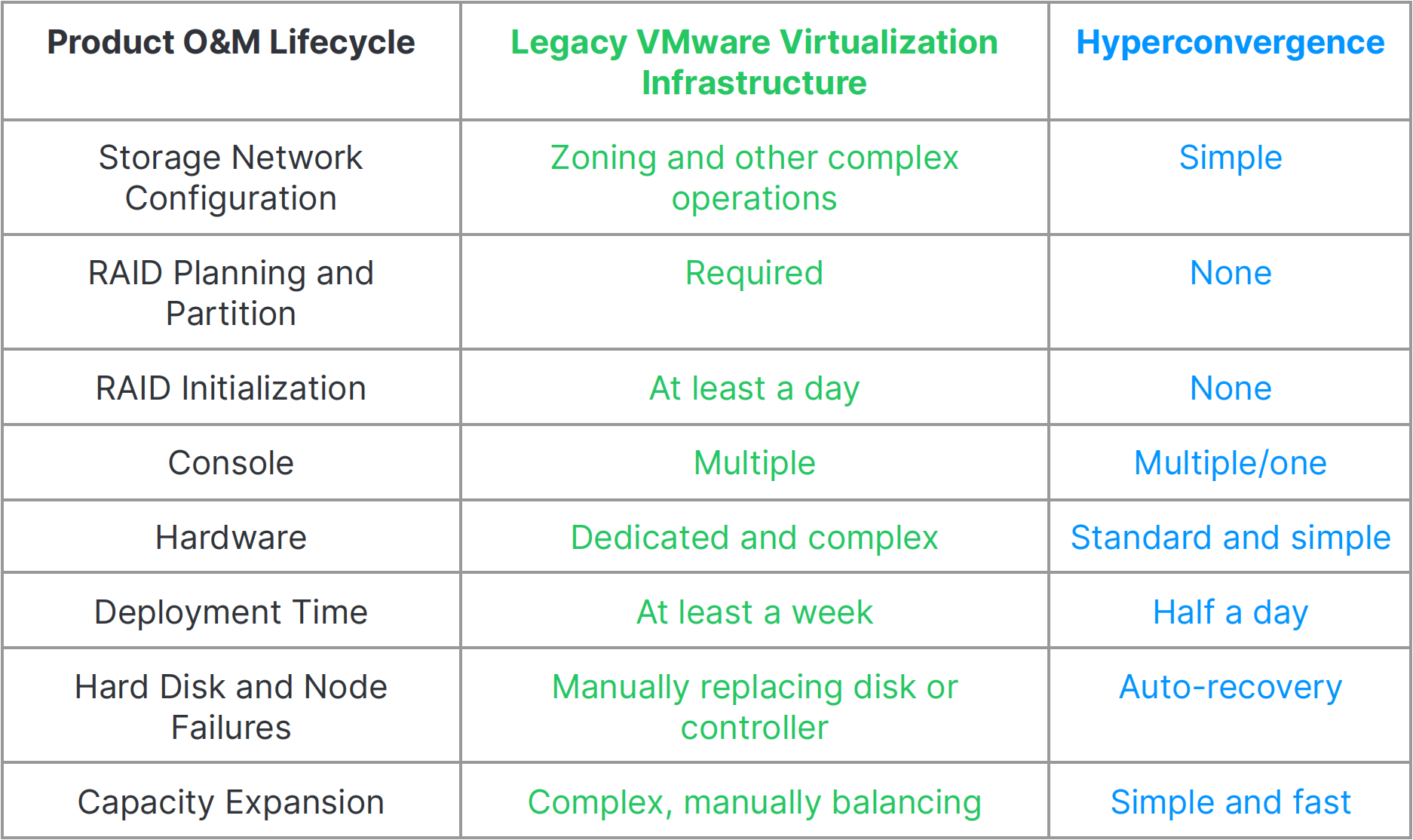
- Reduced difficulty of operation and maintenance
With respect to the ease of O&M, we can compare the two architectures’ entire O&M lifecycle.
As shown in the figure above, hyperconvergence simplifies and automates many operations throughout the entire product O&M lifecycle, which not only improves the overall efficiency of the IT system, but also reduces IT management workload and frees IT professionals to focus on other priorities and innovative works.
- Reduced procurement costs and total cost of ownership
As one of customers’ major concerns, the procurement cost of servers and hyperconvergence software (or hyperconverged infrastructure appliance) is much lower than that for servers plus traditional medium- and high-end storage. Besides, hyperconvergence also requires lower total cost of ownership.
Here we compare the energy consumption of the two architectures with similar computing and storage capacity:
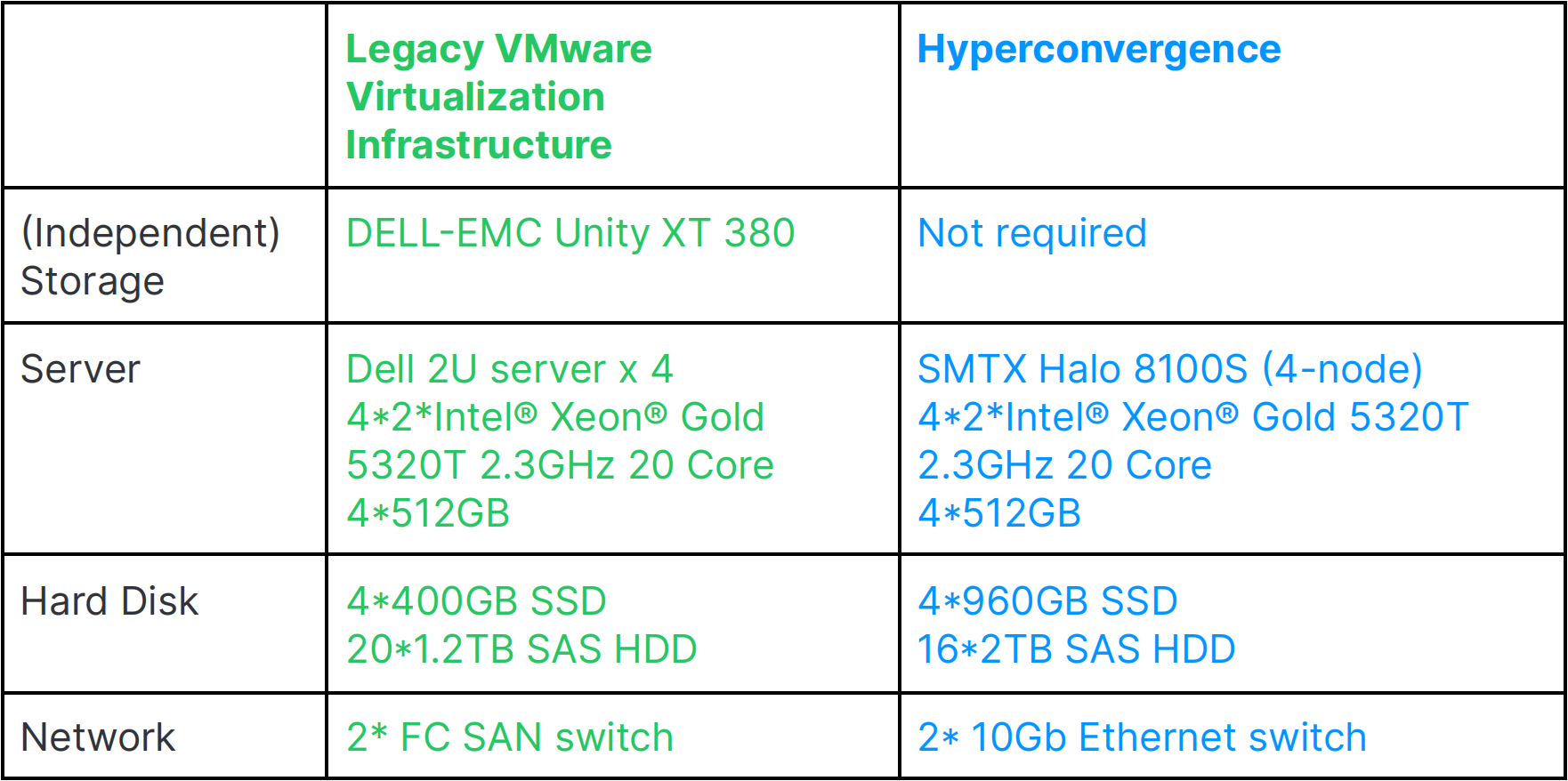 Configuration of the two architectures
Configuration of the two architectures
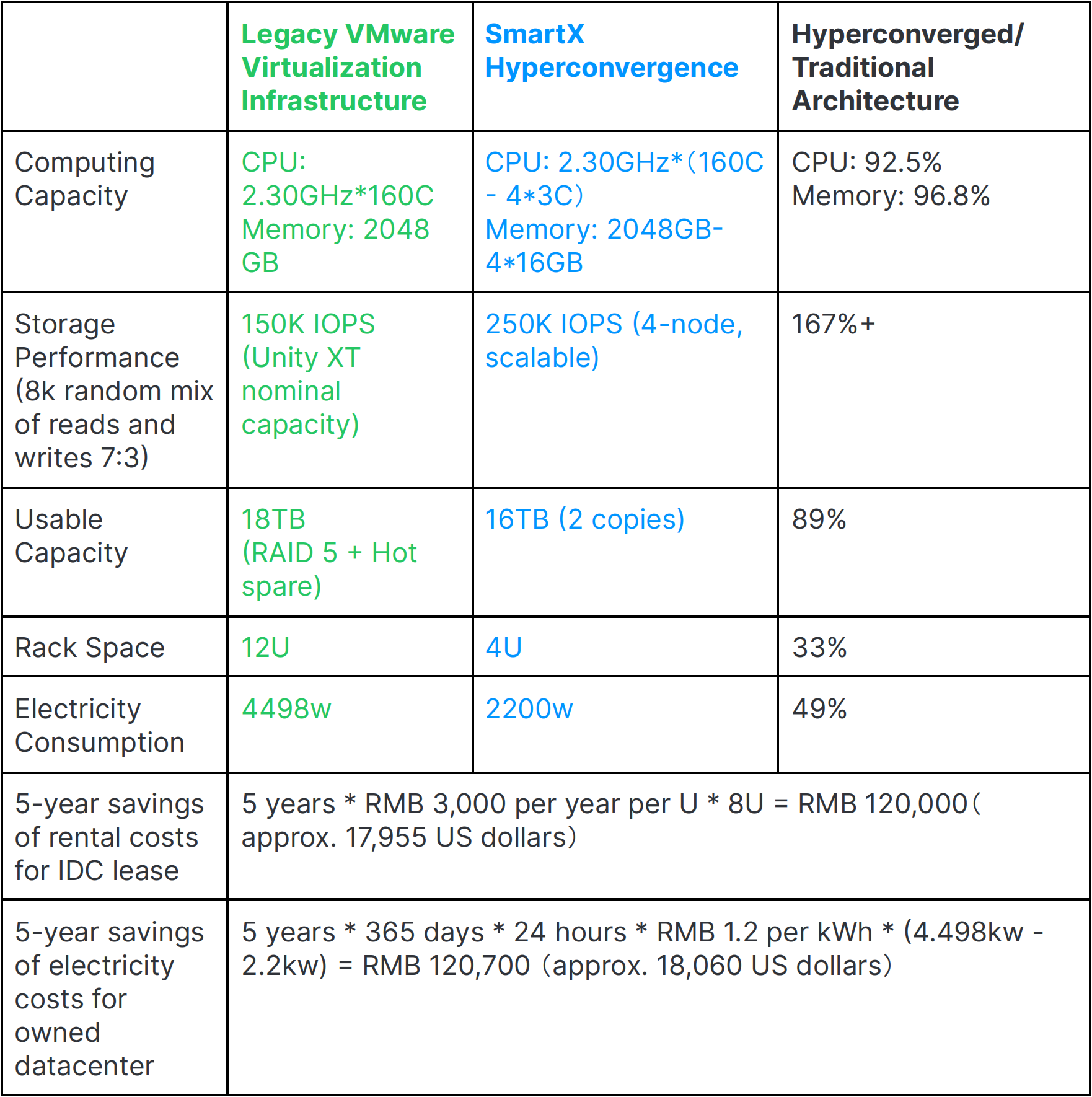 Energy consumption of the two architectures
Energy consumption of the two architectures
To sum up, with its innovative architecture, high performance, excellent scalability, intelligent management and superior cost-effectiveness, hyperconvergence makes IT infrastructure more agile and powerful, accelerating enterprises’ digital transformation.

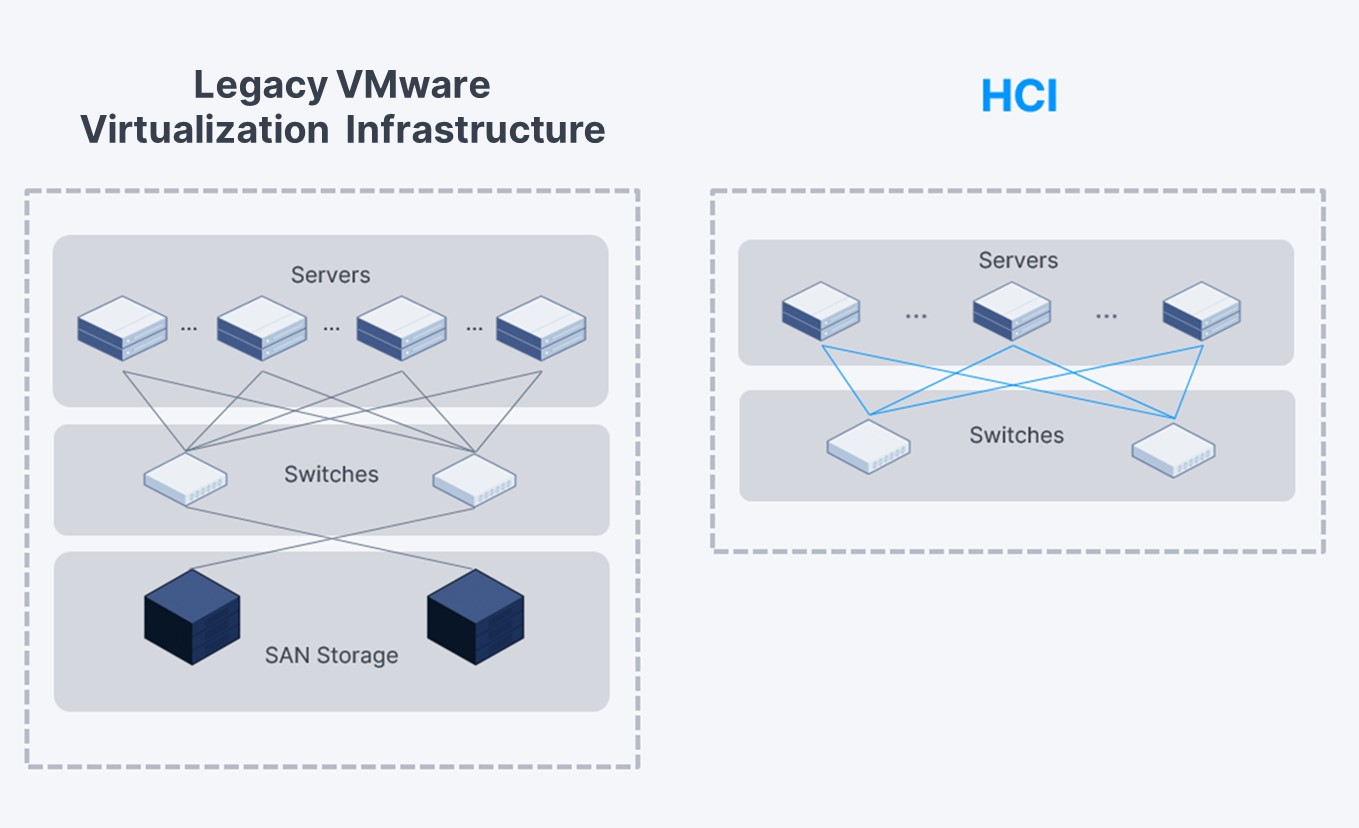 Comparison of architecture
Comparison of architecture